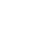Acoustics of Granular Media
Acoustics of Granular Media
Acoustics of Granular Media
Topological Mechanics and Nonlinearity
Although first related to electrons, the fast-developing field of topological insulators has spurred the relevant research also in classical settings, for example, in acoustics and mechanics. This revealed a plethora of classical wave setups with robust localization and transfer of sound -- potentially offering novel applications in energy harvesting, vibration isolation, and phononic waveguiding.
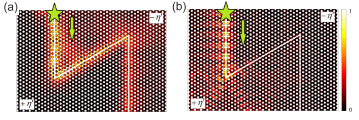
Using simple one and two-dimensional, topological, mechanical lattices, we are trying to reveal and understand intriguing topological, phenomena, such as disorder- and amplitude-dependent topological transitions, non-adiabatic transfer of topological states, and the existence and stability of nonlinear edge and gap solitons.
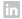
Fig .1 (a) Topologically nontrivial and (b) trivial interface mode in a mechanical granular graphene, (c-e) stable nonlinear topologically nontrivial edge mode
Nonlinear Flexible Elastic Metamaterials
Flexible elastic metamaterials (flexEM) can be defined as artificial, architected structures possessing the ability to deform substantially, repeatedly and reversibly. In recent years, flexEM have undergone rapid developments in their uses and applications, like in the context of soft robotics, innovative actuation (locomotion, grasping), mechanical switching and precise motion control, or large-scale reconfiguration.
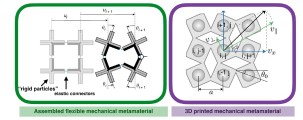
Among all the possible flexEM designs, we are interested in the one composed of rotating masses, such as those shown in Fig. 2.
Indeed, the coexistence of two/three degrees of freedom per site (translations and rotations) and the strong geometrical non-linearity originating from the large rotations, give rise to novel nonlinear phenomena in such architectures, such as vector elastic pulse solitons and transition waves. The latter have in particular proven their interest in the macroscopic reconfiguration of a bistable flexEM.